We selected 22 basic questions about prostatitis and its treatment. All responses were written by our leading male health specialist, andrologist. We hope this article helps him and provides the necessary answers to his questions.
Symptoms of prostatitis: pain, burning, discharge, burning, incontinence
Symptoms of prostatitis are most often of 3 types:
- violation of urination: difficult, frequent night urination.
- pain symptoms: pain in the perineum, lower abdomen, groin. Pain may radiate (radiate) to the scrotum or sacrum.
- mixed form, in which there are urinary disorders and pain.
What causes prostatitis?
with bacterial prostatitis
The infection enters the prostate through neighboring organs:
- urethra;
- Bladder
- through the blood and lymph vessels of a remote inflammatory focus (tonsillitis, sinusitis, caries).
The bacteria most commonly detected in prostatitis are: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Proteus, Staphylococcus aureus, Enterococcus.
The role of sexually transmitted infections is discussed: Chlamydia, Mycoplasma, Trichomonas.
The activity and, consequently, the manifestation of the inflammatory process depend on the properties of the microorganism, the state of the pelvic organs, its blood circulation, concomitant diseases and other predisposing factors.
With non-bacterial prostatitis
Stagnation plays an important role. Violation of blood flow causes edema, exudation of prostate tissue and creates conditions for the development of an inflammatory process that is not associated with a bacterial agent.
STDs and prostatitis
The issue of the involvement of sexually transmitted infections in the development of prostatitis is widely discussed in scientific medical circles. There is no consensus on this matter.
We consider ourselves supporters of a direct connection between infections, the onset and course of prostatitis.
Why is prostatitis dangerous?
Prostatitis is not a threat to the patient's life, the process is chronic and worsens the quality of life.

Early prostatitis. How to determine? first signs
The first signs of prostatitis are changes in the nature of urination: difficulty urinating, frequent urge to urinate, especially at night. Discomfort when urinating and pain of varying intensity in the groin area.
Age of prostatitis? Is this a disease of young and/or elderly people?
Prostatitis is an inflammatory disease, so it can occur at any age. But adenoma or hyperplasia of the prostate is an age-related disease in men after the age of 50 and is associated with the development of a benign prostate tumor.
Chronic prostatitis. Is it possible to cure?
The presence of a diagnosis of chronic prostatitis implies the presence of alterations in the structure of the gland's tissues, which remain throughout life. Like any chronic illness, prostatitis proceeds with alternating periods of exacerbation and remission - a period when the patient is not worried about anything. With proper treatment and lifestyle, remission periods can be very long and complaints never bother the patient again.
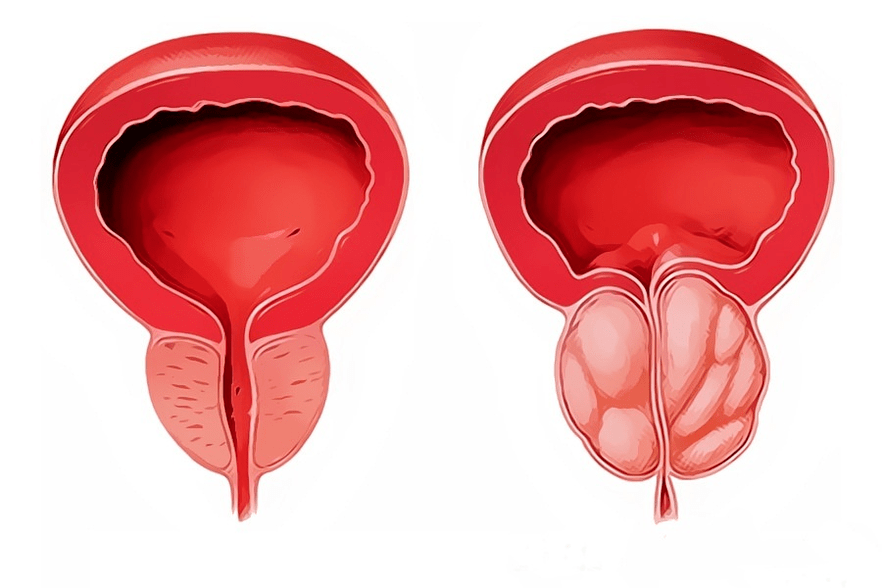
Bacterial and other types of prostatitis
There are several classifications, the most commonly used was developed by the US Institutes of Health in 1995:
- Category I.Acute prostatitis.
- Category II.Chronic bacterial prostatitis.
- Category III.Nonbacterial Prostatitis Syndrome/Chronic Pelvic Pain - No obvious signs of infection and lasting for 3 months or more.
- Subcategory III A.Chronic inflammatory pelvic pain syndrome (with leukocytes in prostate secretion and pathogen excretion).
- Subcategory III B.Chronic non-inflammatory pelvic pain syndrome (no leukocytes in the prostate secret).
- Category IV.Asymptomatic prostatitis (with leukocytes in the prostate secret, but no complaints).
For ease of understanding, the classification can be presented in 3 types:
acute prostatitis- continues with severe pain, fever, urinary disturbances. The secret of the prostate is a large number of leukocytes, which indicates a clear inflammatory process. It usually occurs for the first time in a given patient. If these symptoms occur in a patient with chronic prostatitis, they are called exacerbation of chronic prostatitis.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis- Symptoms that periodically disturb the patient are, as a rule, less pronounced than in acute prostatitis. By diagnosing an increase in leukocytes in the secret prostate, it is possible to identify the causative agent of inflammation.
The most problematic for diagnosis isnon-bacterial prostatitis, or so calledchronic pelvic pain syndrome. . . This is because the complaints are very similar to those of prostatitis, but associated with diseases of other organs and systems, in which it is not possible to detect signs of inflammation and pathogenic bacteria: pelvic muscle spasm, impaired interaction between bladder muscles and its sphincter, anatomical disorders - strictures (narrowing) of the urethra, leads to inflammation due to increased pressure within the lobes of the prostate.
Who Treats Prostatitis - Andrologist or Urologist?
Prostatitis is treated by a urologist and an andrologist.
An andrologist is a urologist who specializes in male reproductive and reproductive diseases.
Treatment methods and regimens for prostatitis
All prostate treatment regimens consist of medications:
- anti-inflammatory
- anti-bacterial
- biogenic stimulants
- drugs that improve prostate and bladder contraction while relaxing the sphincter.
Good results are obtained by the simultaneous consultation of medications and physiotherapy (prostate massage, complexes for the treatment of prostatitis).
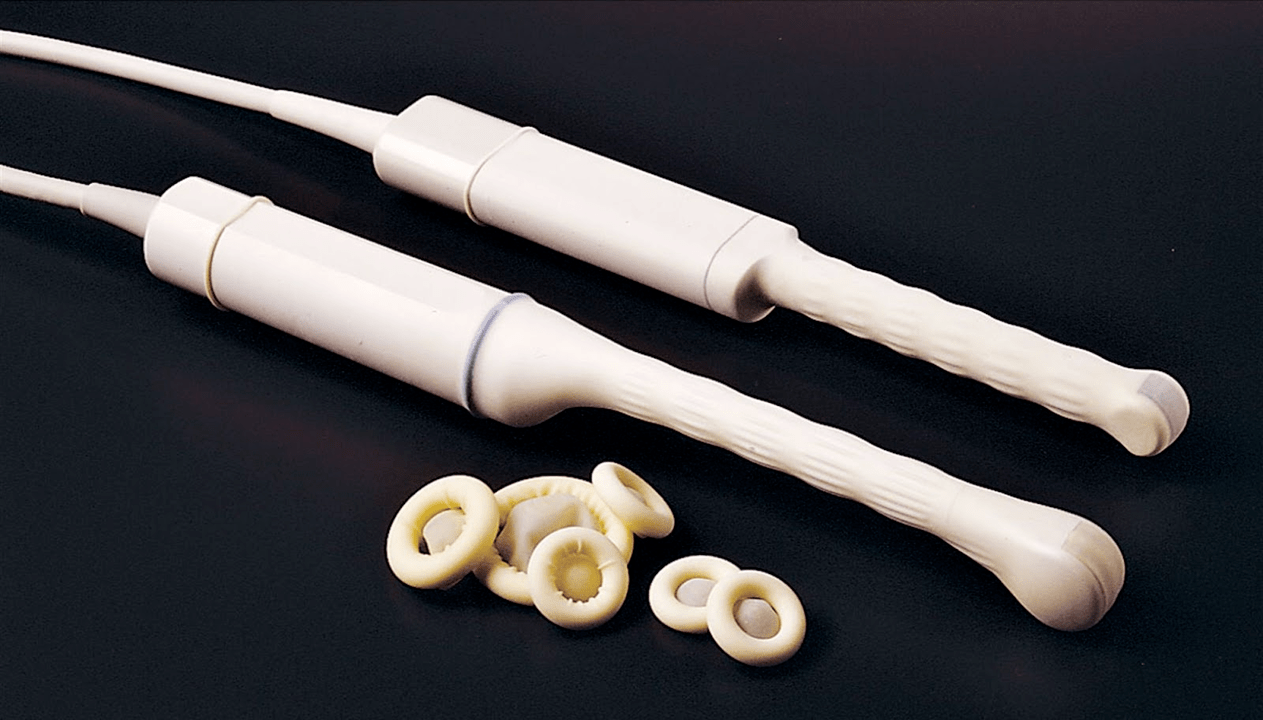
What tests are given for prostatitis?
Forprostatitis diagnosisConsultation with a urologist (andrologist) is necessary to collect the patient's complaints, medical history, microscopy of prostate secretions, and ultrasound diagnosis.
For diagnosis, transrectal prostate ultrasound (TRUS) and prostate secretions obtained after prostate massage are used for microscopic examination.
In addition, the seeding of prostate secretion in the bacterial flora can be used to determine the sensitivity of the seeded microflora to antibiotics.
Surgical interventions and operations for prostatitis
With prostatitis, operations are practically unused. With the exception of prostate abscess - a process in which foci with purulent content are formed.
Is it possible to cure prostatitis alone?
In the presence of severe symptoms, it is best to be treated by a specialist, the time factor plays a large role in the treatment, as the longer the inflammation lasts, the greater the likelihood of irreversible changes in the organ.
But it is better to do the prevention yourself, no doctor will do it for you.
Avoid hypothermia, congestion from sitting for too long, sexually transmitted infections, irregular sexual activity - all these are the path to effective prevention of prostatitis.
Medicines for prostatitis: finalgon, vitaprost, prostamol, ceftriaxone, doxycycline, omnix and others
Drugs for the treatment of prostatitis are divided into groups according to their mechanism of action:
Antibacterial agents (antibiotics)are prescribed only if there is a diagnosis: chronic bacterial prostatitis. The most commonly used fluoroquinolones, macrolides and the doxycycline group of drugs.
Alpha Blockers:are prescribed to restore impaired urination by increasing bladder contraction and relaxing its detrusor.
big groupbiogenic stimulants and herbal preparations: candles.
Effective treatment is only possible with the correct diagnosis, as there are no universal medications for all types of prostatitis. Often, patients take medication to treat prostatitis if they have a completely different disease with similar symptoms.

Nuts, roots, parsley, cucumber, honey, bees, leeches and other popular treatments for prostatitis
Traditional methods of treatment have a right to exist, but you need to understand that it is very difficult to choose a popular method that is right for you. On request, the search engine gives 70 million results for treating prostatitis with popular methods.
No one has researched popular methods for effectiveness. The fact that you have helped a patient with such a treatment (and if you have) does not mean that it will help.
Exacerbation of prostatitis after treatment. remission, relapse
All chronic inflammatory processes have periods of exacerbation and remission, when the patient is not worried about anything. The duration of remission can vary and depends on many factors, including whether the patient is on prophylactic treatment. Patients who undergo preventive treatment periodically without waiting for a worsening in well-being, as a rule, have rarer exacerbations.

Prostate massage at home. Is massage always necessary for prostatitis?
Prostate massage can also be done at home if you are married to a urologist nurse. Any medical manipulation has its own subtleties and nuances. Only a physician can determine the indications for this procedure, therefore, for some diseases: prostate adenoma (in the presence of acute urinary retention), prostate massage is not desirable and, in the case of tumors, it is contraindicated.

alcohol and prostatitis
Alcohol by itself does not cause the development of prostatitis, but it is a factor that increases congestion and swelling in the prostate and thus contributes to its development.
sex life and prostatitis
There is a direct link between the intensity of sexual activity and prostate disease. With prolonged abstinence in the prostate, stagnation occurs, which aggravates metabolic processes and impairs blood microcirculation, contributing to the development of inflammatory processes. Regularity is more important to prostate health than the intensity of sexual intercourse. Excessive sexual intercourse, especially with different partners and unprotected from infections, is the fastest way to prostatitis.

Does prostatitis affect women?
Of course, there is an effect on the health of a woman with prostatitis on a partner. The prostate, along with the seminal vesicles, produces a liquid component of sperm, which, during intercourse, enters the partner's genital tract. The main danger could be the presence of a sexually transmitted infection or bacterial prostatitis, which can cause inflammatory diseases in women.
Pregnancy and prostatitis
Because the prostate produces a liquid part of sperm that contains nutrients for sperm, prostatitis often causes a decrease in sperm quality, which makes it difficult to get pregnant.
Prevention. What to do to prevent prostatitis?
Prevention is directly related to the patient's climate and profession.
Prevention of prostatitis consists of avoiding and minimizing the factors that contribute to the development of prostatitis. It is necessary to avoid hypothermia, alternate sedentary work with periods of physical activity. Regular sex life is important for prostatitis.
























